
2B. Mushlings
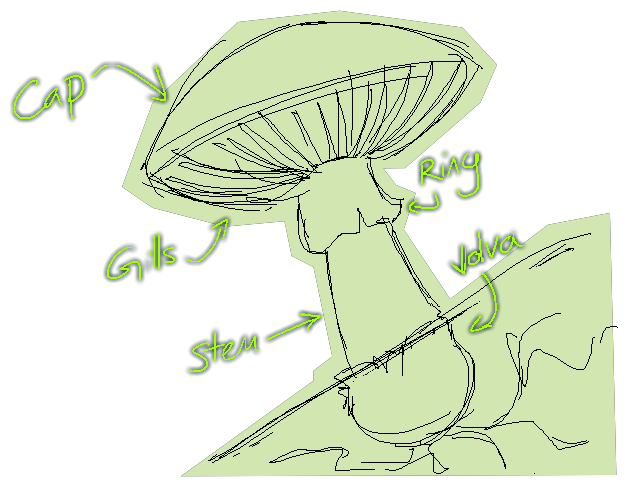
Mushrooms are the fruiting body found on fungi including a stem, a cap, and gills.
However this list can be altered depending on the species as some mushrooms do differ in
features such as the stem being missing or additional features unique to the species.
Mushroom growth is achieved via spores which emit from the gills and underneath the fruiting
body is an underground root system labeled the Mycelium, this root system is what is responsible
for the storage of harmful gases such as carbon dioxide which it produced during the rot and decay
process that fungi help to progress. Much like the other fungi mentioned, Mushrooms are just as
important in the breaking down of organic waste and without them alot of these storaged gasses
would be released into the atmosphere, adding to the effect of green house gasses that
effect us now more than ever already!
Of course on top of its uses in the ecosystem, mushrooms are used by us as a valuable
source for food, given that it is not of the toxic variety of mushrooms (which are labled as
Toadstools). Mushrooms are very important to us and our natural diet, supplying us with alot of
nutrients such as vitamins, potassium, fibres and a general boost alot of important functions,
improving immune systems, brain function, gut health and heart health!
Mushrooms in Fungaloids
Mushrooms are incredibly diverse and can show up in a vast array of shapes and forms,
and accompanying them are a huge array of different protective tactics and behaviours.
This means that Fungaloids with Mushrooms present within their funga pool are bound to look
wildly different than one another and by far have the biggest amount of creative liberty!
To seperate Mushrooms by types would take far too long so instead Mushling Fungaloids are
defined by how the funga pool affects their growth and shape!

2Ba. Clusters
Mushlings with clusters are usually caused by the mushrooms present in the funga pool being
secondary to another fungal type, with the main base of the fungaloid being the other type and
the mushroom cluster coming after them. Because of this, mushlings with clusters tend to be listed
under that primary type rather than as a mushling.
Since this type is usually secondary, the main base of the body and other main characteristics
belong to that primary type and not the clusters.

2Bb. Full Body
Full body Mushlings however are more often than not pure mushroom, or at the very least have
mushrooms as their primary typing or as an overwhelming majority, this full-body style can
be mixed with other types due to the mushroom usually forming in an armour-like fashion given the
mushling a stronger defence than most. On this larger scale the mushroom formed on mushlings is
hard and sturdy, with exact density and toughness being dependent upon species. Unfortunately
this has the unwanted side-effect of making the mushling alot less dexterous and flexible.

See the adoptables page for more examples of fungaloids!
